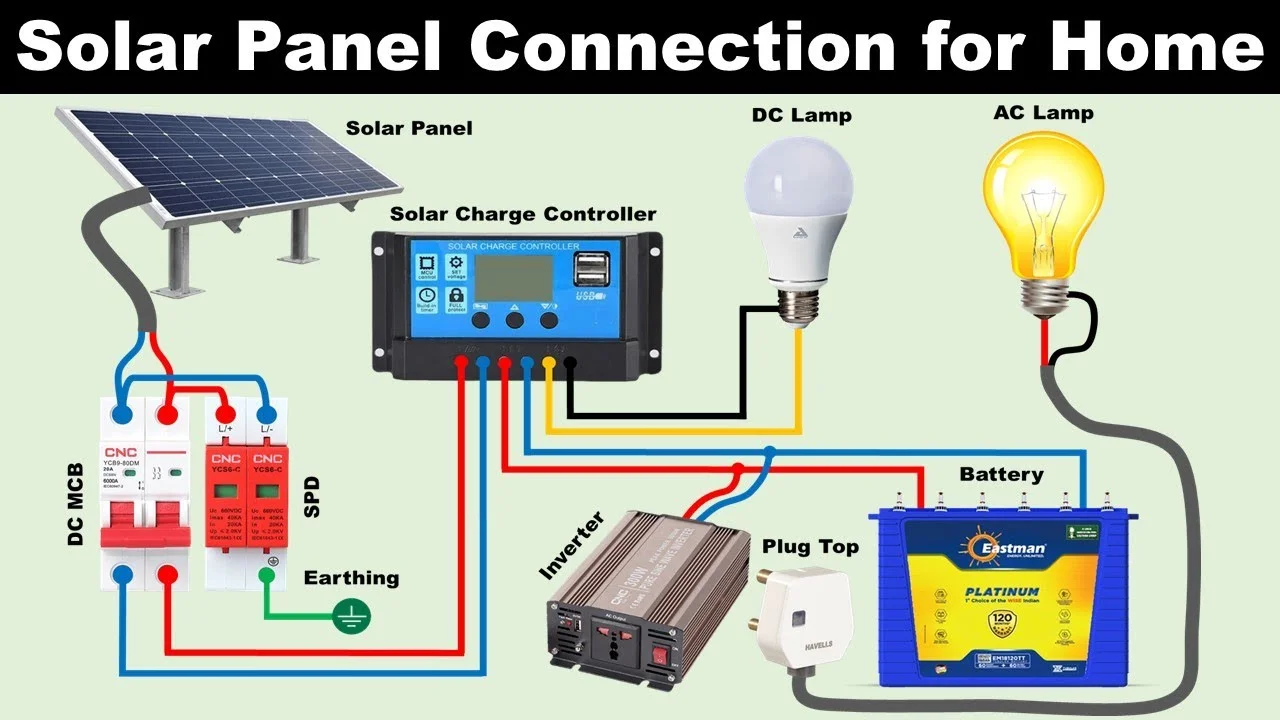
Solar Panel Net Metering: Selling Excess Energy Back to the Grid
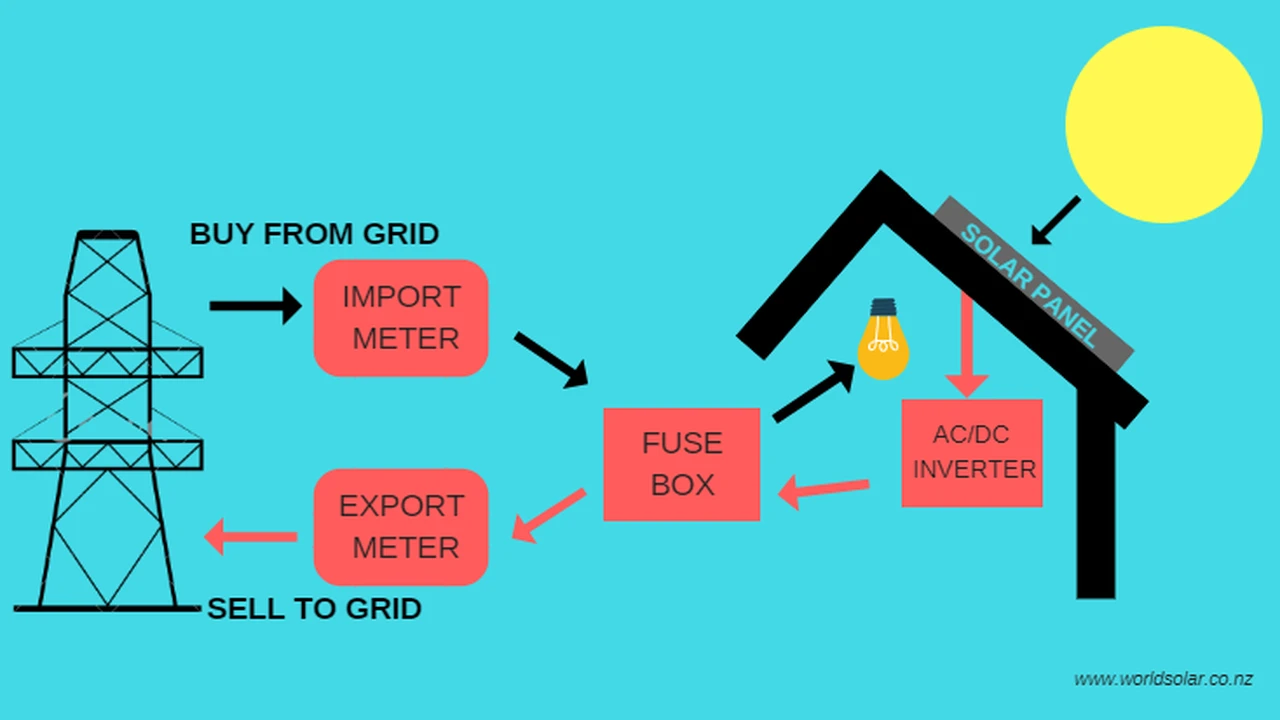
Understanding Solar Panel Net Metering Basics
So, you're thinking about going solar? Awesome! One of the coolest things about having solar panels is the potential to not just power your home, but also make some money while doing it. That's where net metering comes in. Basically, net metering is an agreement with your utility company that allows you to send excess electricity generated by your solar panels back to the grid. When your solar panels produce more electricity than you're using, that extra energy flows back into the grid, and your utility company credits your account. Think of it as selling your extra sunshine!
This is a game-changer because it can significantly reduce your electricity bills, and in some cases, even eliminate them completely. On days when your solar panels are cranking out a lot of power, you might actually be generating more electricity than you're using. Instead of that excess energy going to waste, it's sent back to the grid, and you get credit for it.
How Net Metering Works A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's break down how net metering actually works, step-by-step:
- Solar Panel Installation: First, you get solar panels installed on your roof (or somewhere else on your property).
- Electricity Generation: Your solar panels start generating electricity from sunlight.
- Home Consumption: You use the electricity generated by your solar panels to power your home appliances, lights, and everything else.
- Excess Energy Export: If your solar panels generate more electricity than you're using, the excess energy is automatically sent back to the grid through your existing electricity meter.
- Meter Measurement: Your electricity meter (or a special net meter) measures the amount of electricity you're using from the grid and the amount of electricity you're sending back to the grid.
- Monthly Credit: At the end of the month, your utility company calculates the difference between the electricity you used and the electricity you sent back. You'll be credited for the excess electricity you sent back to the grid, usually at the same rate you pay for electricity.
It's important to note that the specific rules and regulations for net metering can vary depending on your location and your utility company. Some utility companies may offer different rates for the electricity you send back to the grid, and some may have limits on the amount of electricity you can send back.
Benefits of Net Metering For Solar Panel Owners
Net metering offers a ton of benefits for solar panel owners:
- Reduced Electricity Bills: This is the big one. By sending excess electricity back to the grid, you can significantly reduce your electricity bills, and potentially even eliminate them.
- Faster Return on Investment: Net metering helps you recoup your investment in solar panels faster. The credits you receive for sending excess electricity back to the grid can offset the cost of your solar panel system.
- Environmental Benefits: By using solar energy and reducing your reliance on fossil fuels, you're helping to reduce your carbon footprint and protect the environment.
- Increased Home Value: Studies have shown that homes with solar panels tend to have a higher resale value. Net metering makes solar panels even more attractive to potential buyers.
- Energy Independence: Solar panels and net metering can give you more control over your energy costs and reduce your dependence on the utility company.
Choosing the Right Solar Panels For Net Metering
Choosing the right solar panels is crucial for maximizing the benefits of net metering. Here are a few things to consider:
- Efficiency: Look for solar panels with high efficiency ratings. This means they'll generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight.
- Durability: Choose solar panels that are built to last. Look for panels with long warranties and a proven track record of performance.
- Cost: Solar panel prices can vary widely. Compare prices from different manufacturers and installers to find the best deal.
- Warranty: Pay close attention to the warranty offered by the solar panel manufacturer. A good warranty will protect you against defects and performance issues.
Recommended Solar Panel Products for Net Metering
Okay, let's dive into some specific solar panel recommendations. Keep in mind that prices can vary depending on location, installer, and any available incentives or rebates. Also, I'm giving approximate prices based on current market trends, so always get a quote from a reputable installer for an accurate estimate.
SunPower A-Series: High Efficiency and Premium Performance
Description: SunPower is known for its high-efficiency panels, and the A-Series is their top-of-the-line offering. These panels boast some of the highest efficiency ratings on the market, meaning you'll generate more electricity from a smaller area. They also have an excellent reputation for durability and reliability.
Typical Usage Scenario: Ideal for homeowners with limited roof space or those who want to maximize their energy production. Perfect for net metering scenarios where you want to send as much excess energy back to the grid as possible.
Comparison: SunPower panels are generally more expensive than other brands, but their superior efficiency and performance can justify the higher cost, especially in net metering situations. They often outperform standard panels by 10-15% in energy production over their lifespan.
Approximate Price: $3.00 - $4.00 per watt (installed)
Panasonic EverVolt Series: Reliability and Excellent Warranty
Description: Panasonic EverVolt panels are another excellent choice, known for their reliability and comprehensive warranty. They offer a good balance of efficiency, performance, and cost.
Typical Usage Scenario: A solid choice for homeowners looking for a reliable and long-lasting solar panel system. Suitable for various climates and roof types. Great for those who value a strong warranty and peace of mind.
Comparison: Panasonic panels offer a competitive price point compared to SunPower, with slightly lower efficiency but still excellent performance. Their warranty is a major selling point, often covering performance for 25 years with a low degradation rate.
Approximate Price: $2.75 - $3.50 per watt (installed)
REC Group Alpha Series: High Power and Innovative Design
Description: REC Group's Alpha Series panels feature an innovative design that maximizes power output. They're known for their high power density, meaning they can generate more electricity from a smaller panel size.
Typical Usage Scenario: Suitable for homes with limited roof space or those who want to maximize their energy production without compromising on aesthetics. Their high power output makes them a good choice for net metering, allowing you to send more electricity back to the grid.
Comparison: REC panels offer a good balance of performance and cost, often falling in between SunPower and Panasonic in terms of price. They are known for their robust build quality and consistent performance.
Approximate Price: $2.50 - $3.25 per watt (installed)
Q CELLS Q.PEAK DUO Series: Cost-Effective and Reliable
Description: Q CELLS Q.PEAK DUO panels are a more budget-friendly option that still offers good performance and reliability. They are a popular choice for homeowners looking for an affordable solar panel system.
Typical Usage Scenario: Ideal for homeowners on a tighter budget who still want to benefit from solar energy and net metering. A good option for homes with ample roof space where efficiency is less of a concern.
Comparison: Q CELLS panels are generally less expensive than the other brands mentioned above, but their efficiency is also slightly lower. However, they still offer a good return on investment, especially when combined with net metering.
Approximate Price: $2.00 - $2.75 per watt (installed)
Different Solar Panel Types and Their Impact on Net Metering
There are different types of solar panels, each with its own characteristics. The most common types are:
- Monocrystalline: These are the most efficient and expensive type of solar panel. They're made from a single crystal of silicon, which allows them to generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight.
- Polycrystalline: These are less efficient and less expensive than monocrystalline panels. They're made from multiple crystals of silicon.
- Thin-Film: These are the least efficient and least expensive type of solar panel. They're made by depositing a thin layer of photovoltaic material onto a substrate.
For net metering, monocrystalline panels are generally the best choice because they generate the most electricity. However, polycrystalline panels can also be a good option if you're on a tighter budget.
The Importance of Solar Inverters for Net Metering
A solar inverter is a critical component of any solar panel system, and it plays a key role in net metering. The inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by your solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the type of electricity used in your home and by the grid.
There are two main types of solar inverters:
- String Inverters: These are the most common type of solar inverter. They connect to a string of solar panels and convert the DC electricity from the entire string into AC electricity.
- Microinverters: These are small inverters that are installed on each individual solar panel. They convert the DC electricity from each panel into AC electricity separately.
Microinverters offer several advantages over string inverters, including:
- Improved Performance: Microinverters can optimize the performance of each individual solar panel, which can lead to higher overall energy production.
- Increased Reliability: Microinverters are more reliable than string inverters because if one microinverter fails, it won't affect the performance of the other panels.
- Easier Monitoring: Microinverters allow you to monitor the performance of each individual solar panel, which can help you identify and troubleshoot any problems.
For net metering, microinverters are generally the best choice because they can help you maximize your energy production and ensure that you're sending as much electricity back to the grid as possible.
Net Metering Policies By State Understanding the Regulations
Net metering policies vary significantly from state to state. Some states have very generous net metering policies, while others have less favorable policies. It's important to understand the net metering policies in your state before you invest in solar panels.
Some key factors to consider include:
- The rate at which you're credited for excess electricity: Some states require utility companies to credit you at the full retail rate for excess electricity, while others allow them to credit you at a lower rate.
- The amount of excess electricity you can send back to the grid: Some states have limits on the amount of excess electricity you can send back to the grid.
- The availability of net metering: Some states have limits on the number of customers who can participate in net metering programs.
You can find information about the net metering policies in your state by contacting your utility company or your state's energy office.
Solar Panel Installation and Net Metering Connecting To The Grid
The process of installing solar panels and connecting them to the grid for net metering typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation and Design: A solar installer will assess your energy needs and design a solar panel system that meets your requirements.
- Permitting: The installer will obtain the necessary permits from your local government and utility company.
- Installation: The installer will install the solar panels on your roof or other location.
- Inspection: A building inspector will inspect the installation to ensure that it meets all safety and code requirements.
- Interconnection: The installer will connect your solar panel system to the grid.
- Net Metering Agreement: You'll sign a net metering agreement with your utility company.
It's important to choose a reputable solar installer who is familiar with the net metering policies in your state. They can guide you through the process and ensure that your solar panel system is properly installed and connected to the grid.
Maximizing Your Solar Panel Investment Through Net Metering
Net metering is a powerful tool that can help you maximize your investment in solar panels. By understanding how net metering works and choosing the right solar panels, inverters, and installer, you can significantly reduce your electricity bills, generate income from your excess energy, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Remember to research your state's net metering policies and compare quotes from multiple installers to find the best deal. With a little planning and effort, you can make the most of your solar panel system and enjoy the benefits of net metering for years to come.
Troubleshooting Common Net Metering Problems
Even with a well-designed and installed solar panel system, you might encounter some common net metering issues. Here's a quick rundown and some potential solutions:
- Unexpectedly High Electricity Bills: Double-check your utility bill to ensure the net metering credits are being applied correctly. Contact your utility company to investigate any discrepancies. Also, consider your energy consumption habits. Has anything changed recently that might be increasing your usage?
- Low Solar Panel Production: Check for any shading on your solar panels. Trees, buildings, or even accumulated dirt can significantly reduce their output. Regularly clean your panels (safely!) and trim back any encroaching vegetation. Also, use your monitoring system (if you have one) to check the performance of individual panels.
- Meter Reading Issues: Make sure your meter is being read correctly. Contact your utility company if you suspect a problem with the meter reading process. Some meters might need to be replaced with net meters, so confirm that yours is the correct type.
- Inverter Problems: A malfunctioning inverter can significantly reduce your solar panel system's output. Check the inverter's display for any error messages and contact your installer or a qualified technician for repairs.
- Grid Outages: During a grid outage, your solar panel system will likely shut down for safety reasons. This is normal. Once the grid power is restored, your system should automatically restart.
The Future of Net Metering and Solar Energy
The future of net metering and solar energy is bright. As solar technology continues to improve and become more affordable, more and more homeowners are turning to solar panels to power their homes and reduce their carbon footprint. Net metering is a key enabler of this trend, making solar energy more accessible and affordable for everyone.
However, net metering policies are constantly evolving. Some utility companies are pushing for changes that would reduce the benefits of net metering for solar panel owners. It's important to stay informed about these developments and advocate for policies that support the growth of solar energy.
With continued innovation and supportive policies, solar energy has the potential to become a major source of electricity in the future, helping to create a cleaner and more sustainable energy future for all.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)