Solar Panel Installation Costs: A Breakdown of Expenses
Understanding the Initial Investment Solar Panel Cost Factors
So, you're thinking about going solar? Awesome! But let's be real, the first thing that pops into most people's heads is: "How much is this gonna cost me?" Solar panel installation costs can seem like a big, scary number at first, but breaking it down makes it much less intimidating. Think of it like buying a car – you wouldn't just walk into a dealership and say, "Give me a car!" You'd want to know about the model, features, and, of course, the price. Solar panels are the same. Let's dive into the key factors that influence the price tag.
First off, the size of your system matters. Obvious, right? A small apartment might only need a few panels, while a large house with high energy consumption will need a much bigger setup. This is usually measured in kilowatts (kW). A 5kW system will cost less than a 10kW system. Think of it like this: the more energy you need, the more panels you'll need, and the more you'll spend. We'll talk more about sizing later.
Next up: the type of panels. Not all solar panels are created equal! There are different types, each with its own efficiency, durability, and, you guessed it, price. Monocrystalline panels are typically more efficient and have a sleeker look (often black), but they also tend to be more expensive. Polycrystalline panels are slightly less efficient and have a blueish hue, but they're generally more budget-friendly. Thin-film panels are another option, often more flexible and sometimes cheaper, but they’re also usually the least efficient, meaning you'll need more of them to generate the same amount of power.
Then there's labor costs. Installing solar panels is not a DIY project for the faint of heart! You'll need qualified installers to handle the electrical wiring, mounting, and permitting. Labor costs can vary depending on your location, the complexity of the installation (e.g., roof type, accessibility), and the installer's rates. Get multiple quotes! This is crucial. Don't just go with the first company you find. Compare pricing and read reviews.
And don’t forget permitting and inspection fees. Your local government will likely require permits for solar panel installations, and they'll want to inspect the system to ensure it meets safety standards. These fees can vary widely depending on your location. Your installer should be able to help you navigate the permitting process.
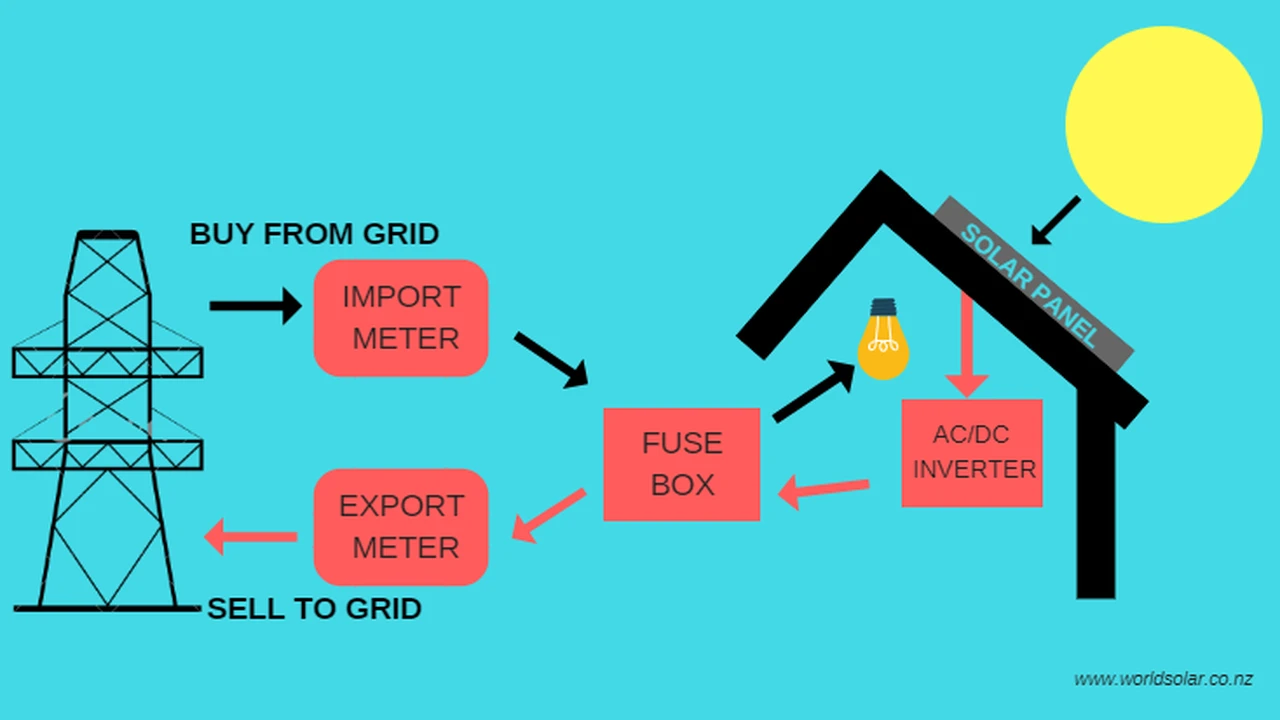
Finally, consider additional equipment. Solar panels are just one piece of the puzzle. You'll also need an inverter to convert the DC electricity generated by the panels into AC electricity that your home can use. You might also need batteries for energy storage (if you want to go off-grid or have backup power), racking systems to mount the panels, and wiring. These additional components all add to the overall cost.
Detailed Cost Breakdown of Solar Panel Installation and Solar Panel System Pricing
Okay, let's get down to brass tacks and talk numbers. The average cost of solar panel installation in the US typically ranges from $2.50 to $3.50 per watt before any incentives or tax credits. So, for a 5kW system, you're looking at a ballpark figure of $12,500 to $17,500. Now, before you faint, remember that this is just an estimate, and the actual cost can vary significantly depending on the factors we discussed earlier.
Let's break down a hypothetical 6kW system for a more concrete example:
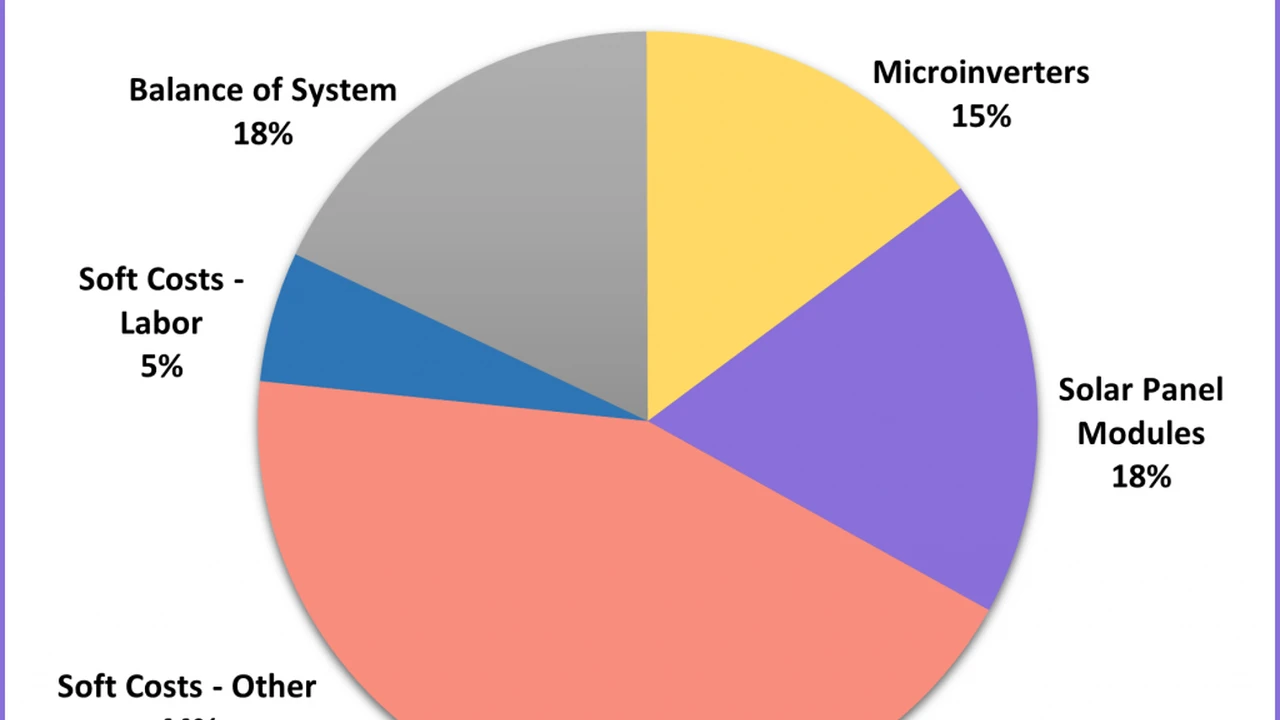
- Solar Panels: $6,000 - $9,000 (depending on panel type)
- Inverter: $1,000 - $2,000
- Racking System: $500 - $1,000
- Labor: $3,000 - $5,000
- Permits & Inspection: $500 - $1,500
- Miscellaneous (Wiring, etc.): $200 - $500
Total Estimated Cost: $11,200 - $19,000
See? It's a range! Getting accurate quotes from multiple installers is the only way to get a true picture of the cost for your specific situation.
Exploring Solar Panel Rebates Incentives and Tax Credits for Solar Panel Owners
Here's the good news: the upfront cost of solar panel installation is often significantly reduced by various incentives, rebates, and tax credits. These incentives are designed to encourage homeowners to adopt renewable energy and can save you a ton of money.
The big one is the Federal Solar Tax Credit (Investment Tax Credit or ITC). This credit allows you to deduct 30% of the cost of your solar panel system from your federal taxes. That's a huge chunk of change! So, if your system costs $15,000, you could get a $4,500 tax credit.
Many states also offer state-level rebates and tax credits. These incentives vary widely from state to state, so it's essential to research what's available in your area. Some states offer upfront rebates, while others offer ongoing tax credits over several years.
Some utility companies also offer rebates or incentives for solar panel installations. Check with your local utility company to see if they have any programs available.
Finally, there are net metering programs. Net metering allows you to sell excess electricity generated by your solar panels back to the grid. This can help you offset your electricity bill and potentially even earn money. The specifics of net metering programs vary depending on your location and utility company.
Example: Let's say you install a $15,000 solar panel system. You get a $4,500 federal tax credit (30%). Your state offers a $1,000 rebate. Your utility company offers a net metering program that credits you for excess energy production. Suddenly, that $15,000 investment looks a lot more manageable!
Choosing the Right Solar Panels Product Recommendations and Performance Comparison
Choosing the right solar panels can feel overwhelming. There are tons of brands and models out there, each with its own specifications and performance characteristics. Here are a few popular brands and models to consider, along with their pros and cons:
REC Group Alpha Series
Pros: High efficiency, excellent temperature coefficient (meaning they perform well in hot weather), durable, and aesthetically pleasing. REC Group is a well-established and reputable manufacturer.
Cons: Relatively expensive compared to other brands.
Typical Use Case: Homeowners looking for maximum energy production and a sleek appearance.
Estimated Price: $3.00 - $3.50 per watt
Panasonic EverVolt Series
Pros: High efficiency, excellent warranty (25 years for both performance and product), and integrated monitoring system. Panasonic is a trusted brand known for quality electronics.
Cons: Can be more expensive than other options.
Typical Use Case: Homeowners who prioritize reliability and a long warranty.
Estimated Price: $3.20 - $3.80 per watt
Q CELLS Q.PEAK DUO Series
Pros: Good balance of performance and price, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. Q CELLS is a global manufacturer with a strong reputation.
Cons: Slightly lower efficiency than REC Group or Panasonic.
Typical Use Case: Homeowners looking for a good value option with reliable performance.
Estimated Price: $2.70 - $3.20 per watt
Silfab Solar Elite Series
Pros: High efficiency, North American made, durable, and aesthetically pleasing with a sleek all-black design. Silfab is known for high quality and performance.
Cons: Can be more expensive than other options.
Typical Use Case: Homeowners wanting to support local manufacturing and looking for high performance panels with a premium look.
Estimated Price: $3.10 - $3.70 per watt
Performance Comparison: Efficiency is a key factor to consider. Higher efficiency panels generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. The temperature coefficient is also important, especially if you live in a hot climate. A lower temperature coefficient means the panel's performance degrades less in hot weather. Warranty is another crucial factor. Look for panels with a long warranty (at least 25 years) for both performance and product defects.
Inverter Selection Considerations and Choosing a Solar Inverter System
The inverter is the brains of your solar panel system. It converts the DC electricity generated by the panels into AC electricity that your home can use. There are two main types of inverters: string inverters and microinverters.
String Inverters
How they work: String inverters connect to a series of solar panels (a "string"). The inverter then converts the DC electricity from the entire string into AC electricity.
Pros: Generally more affordable than microinverters, simpler to install, and easier to troubleshoot.
Cons: The performance of the entire string is limited by the weakest panel. If one panel is shaded or malfunctioning, it can affect the output of the entire string. Less flexibility for system expansion.
Typical Use Case: Homes with unshaded roofs and simple system designs.
Microinverters
How they work: Microinverters are small inverters that are installed on each individual solar panel. Each panel operates independently, maximizing energy production.
Pros: Higher energy production in shaded conditions, greater flexibility for system expansion, and individual panel monitoring.
Cons: More expensive than string inverters, more complex to install, and more components to potentially fail.
Typical Use Case: Homes with shaded roofs, complex system designs, or homeowners who want maximum energy production.
Popular Inverter Brands
- Enphase: A leading manufacturer of microinverters. Known for their high performance and reliability.
- SolarEdge: Offers both string inverters and optimizers (which are similar to microinverters). Known for their advanced monitoring capabilities.
- SMA: A well-established manufacturer of string inverters. Known for their reliability and efficiency.
Solar Panel Installation Location and Roof Orientation for Solar Panel Efficiency
The location and orientation of your solar panels have a significant impact on their energy production. Ideally, you want to position your panels to maximize exposure to sunlight throughout the day.
Roof Orientation: In the Northern Hemisphere, a south-facing roof is generally the best for solar panel installations. This orientation provides the most direct sunlight exposure throughout the day. East-facing roofs can also be a good option, especially for morning energy production. West-facing roofs are better for afternoon energy production. North-facing roofs are generally not recommended, as they receive the least amount of sunlight.
Roof Angle: The optimal roof angle depends on your latitude. In general, a roof angle that is close to your latitude is ideal. For example, if you live at a latitude of 40 degrees, a roof angle of 40 degrees would be optimal. However, a range of angles around the optimal angle will still provide good energy production.
Shading: Shading can significantly reduce the energy production of your solar panels. Avoid installing panels in areas that are shaded by trees, buildings, or other obstructions. If shading is unavoidable, consider using microinverters, which can minimize the impact of shading on the overall system performance.
Financing Options for Solar Panel Installation and Affording Your Solar Panels
Solar panel installation can be a significant investment, but there are several financing options available to help you afford it.
Solar Loans
Solar loans are specifically designed to finance solar panel installations. These loans typically have lower interest rates and longer repayment terms than traditional loans.
Home Equity Loans
Home equity loans allow you to borrow money against the equity in your home. These loans can be used to finance solar panel installations, but they also put your home at risk if you are unable to repay the loan.
Personal Loans
Personal loans can be used to finance solar panel installations, but they typically have higher interest rates than solar loans or home equity loans.
Leasing
Solar leases allow you to lease solar panels from a company. You pay a monthly fee for the use of the panels, but you don't own them. Leasing can be a good option if you don't want to make a large upfront investment, but you won't be eligible for the federal tax credit or other incentives.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
PPAs are similar to leases, but you pay for the electricity generated by the solar panels rather than paying a fixed monthly fee. PPAs can be a good option if you want to save money on your electricity bill without making a large upfront investment.
Long Term Savings and Return on Investment of Solar Panel Installations
While the initial cost of solar panel installation can seem high, the long-term savings and return on investment can be significant.
Reduced Electricity Bills: Solar panels can significantly reduce or even eliminate your electricity bills. The amount of savings will depend on the size of your system, your energy consumption, and the net metering program in your area.
Increased Home Value: Studies have shown that solar panels can increase the value of your home. Buyers are often willing to pay more for a home with solar panels because they know they will save money on their electricity bills.
Environmental Benefits: Solar panels are a clean and renewable source of energy. By installing solar panels, you can reduce your carbon footprint and help protect the environment.
Payback Period: The payback period for solar panel installations is typically 5-10 years. This means that it will take 5-10 years for the savings from reduced electricity bills to offset the initial cost of the system. After the payback period, you will be saving money on your electricity bills for the remainder of the system's lifespan (typically 25-30 years).
Maintenance Requirements and Ensuring Solar Panel Longevity
Solar panels are relatively low-maintenance, but there are a few things you can do to ensure their longevity and optimal performance.
Cleaning: Solar panels can accumulate dirt, dust, and debris over time, which can reduce their energy production. Cleaning your panels periodically (typically once or twice a year) can help maintain their performance. You can clean them yourself with a soft brush and water, or you can hire a professional cleaning service.
Inspections: It's a good idea to have your solar panel system inspected periodically by a qualified technician. The technician can check for any damage, loose connections, or other issues that could affect the system's performance.
Monitoring: Many solar panel systems come with monitoring systems that allow you to track their energy production. Monitoring your system can help you identify any problems early on.
Warranty: Make sure you understand the warranty coverage for your solar panels and inverter. A good warranty will protect you against any defects or performance issues.
Future Trends in Solar Panel Technology and Solar Panel Innovation
The solar panel industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging all the time.
Increased Efficiency: Solar panel manufacturers are constantly working to improve the efficiency of their panels. Higher efficiency panels generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, which means you can install fewer panels to meet your energy needs.
Lower Costs: The cost of solar panels has been declining steadily over the past decade. This trend is expected to continue, making solar panel installations more affordable for homeowners.
Energy Storage: Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are becoming increasingly popular. Energy storage allows you to store excess electricity generated by your solar panels and use it when the sun isn't shining. This can help you become more energy independent and reduce your reliance on the grid.
Perovskite Solar Cells: Perovskite solar cells are a new type of solar cell that has the potential to be even more efficient and cheaper than traditional silicon solar cells. Perovskite solar cells are still in the early stages of development, but they hold great promise for the future of solar energy.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)